Web Hosting
Putting the pieces together:
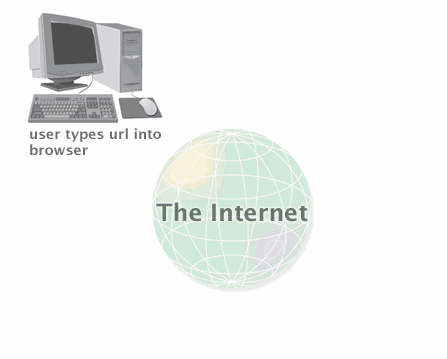
- URL is typed into browser.
- Request is sent to the ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- ISP sends request to Domain Name Resolver to find the appropriate IP address.
- Browser request is then pointed to the Web server with the IP address.
- Web server (host) points to the appropriate data on the computer.
- Web site is displayed through browser.
A Web host provides your Web site with a dedicated IP address. This address is registered with ICANN (the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) to point to your domain name. When a user types a URL into a Web browser, the user's ISP checks with one of thousands of computers known as Domain Name Resolvers. The Resolvers have a database that matches every registered domain name to its unique IP address. The address from that database is passed back to the browser, which then knows which Web server to look for. At the Web server, the IP address is mapped to a particular folder, and the rest of the URL points to a specific file which is displayed.